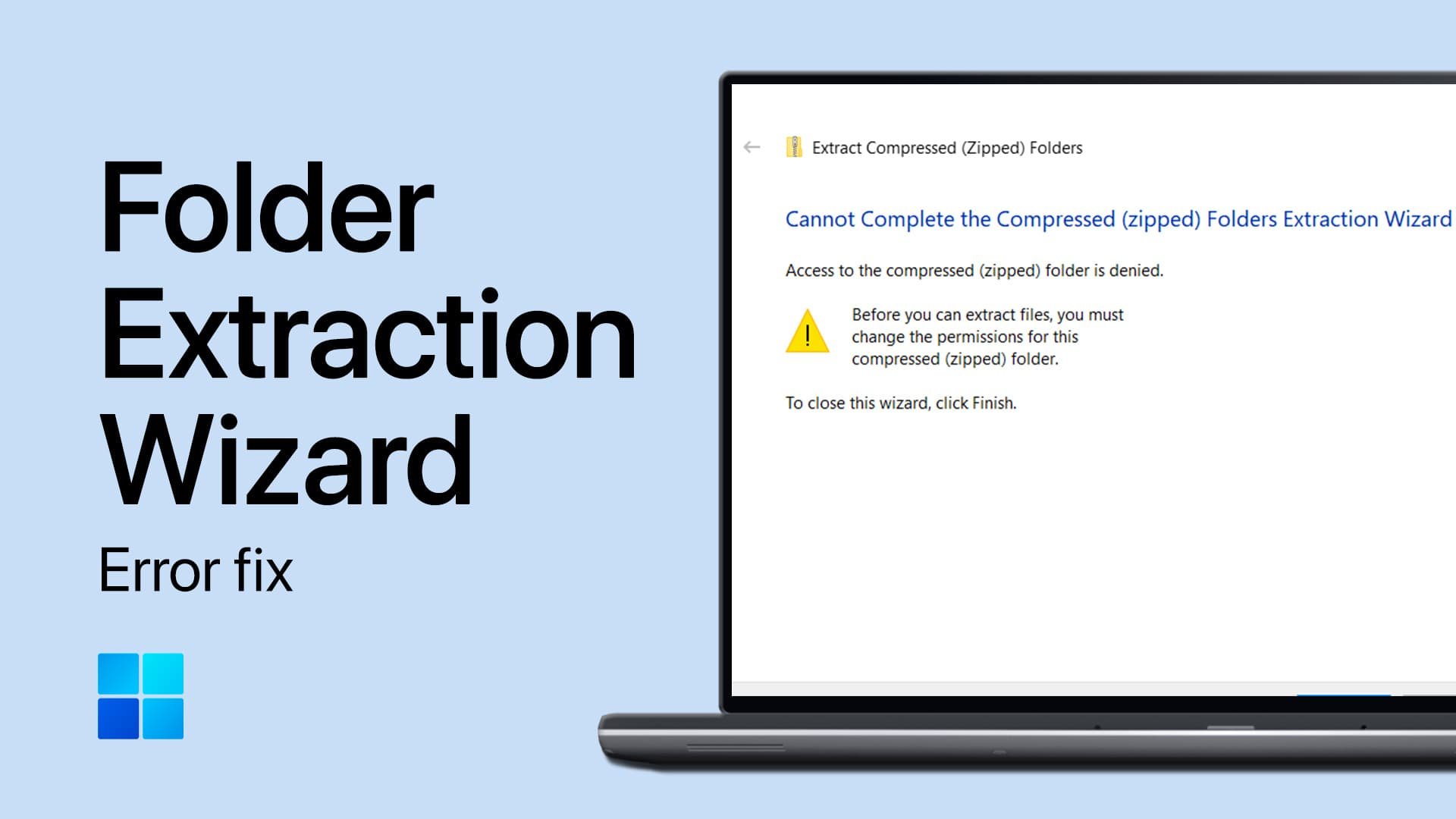
Easiest Ways to Improve your WiFi Connection on Windows PC
Introduction
Struggling with slow or intermittent WiFi on your Windows PC? In a world where the internet has become integral to our daily lives, a sluggish connection can be more than a minor annoyance. Whether you're working from home, attending a virtual meeting, or just trying to enjoy a favorite show, a seamless WiFi connection is key. This article unveils the easiest ways to optimize and enhance your WiFi connection, from simple adjustments like relocating your router to tech-savvy solutions like updating network adapter drivers. Dive in to discover how you can boost signal strength, minimize interference, and make the most of your bandwidth for a smooth and fast internet experience.
Router Placement: Optimize Signal Strength
One of the most straightforward methods to improve your WiFi connection is to optimize the placement of your router. Here's how you can achieve better signal strength:
Position Centrally: Place the router in a central location in your home to ensure equal distribution of the WiFi signal.
Elevate It: Keep the router off the ground, ideally on a shelf or table.
Avoid Obstructions: Stay clear of walls, metal objects, and other obstructions that can block the signal. For example, avoid placing the router behind a TV or near a refrigerator.
Router Update: Enhance Performance and Security
Keep your router functioning at its best by regularly updating its firmware:
Access Settings: Use a web browser to access your router's settings.
Find Updates: Search for available updates by entering your router model in your browser.
Stay Current: Keeping the router's firmware up to date not only improves performance but also enhances security.
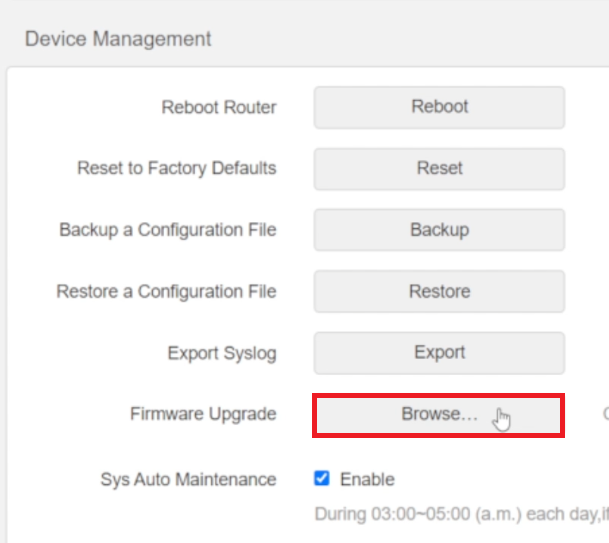
Router Management > Firmware Update
Limit Devices: Manage Bandwidth Consumption
A crowded network can slow down your internet connection. Here's how to manage the devices connected to your router:
Identify Bandwidth Hogs: Check the router settings to see if any devices are consuming more than their fair share of bandwidth.
Tweak Settings: You can limit the bandwidth for specific devices, like streaming gadgets or gaming consoles, to ensure a more balanced distribution of your internet connection. This helps in maintaining a steady connection for priority tasks such as work-related activities or video calls.
Router Management > Administration
Limit Background Apps: Free Up Bandwidth
Unnecessary background applications can hog your bandwidth and slow down your internet connection. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you manage this issue:
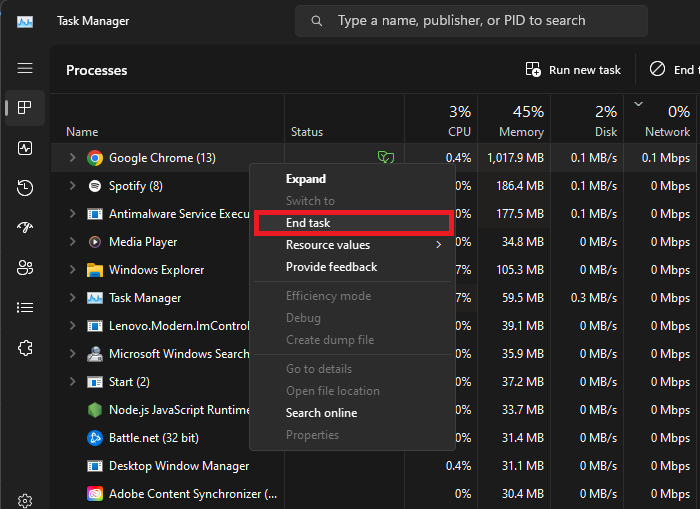
Open Task Manager: Search for 'Task Manager' in your start menu search and open it.
Identify Resource-Intensive Apps: In the “Processes” section, click the ‘Network’ label to sort the programs according to network consumption.
End Unnecessary Processes: Identify and close unnecessary apps that are consuming your network resources. For example, you might find streaming services or large file downloads that can be paused. Make sure to only end the processes that you know won't disrupt your operating system.
Task Manager > Processes > Network
Reduce Interference: Maintain a Strong Signal
Electronic devices like phones and microwave ovens can create interference with your WiFi signal. Here's what you can do to minimize this effect:
Distance from Interfering Devices: Keep these devices away from your router to reduce their impact on your WiFi signal.
Switch to a 5GHz Band: If possible, switch to a 5GHz band on your router for less interference. This option provides a more stable connection but may be unavailable in older routers. Check your router's manual to see if this feature is accessible, as it can significantly enhance your online experience, especially during activities like video conferencing or online gaming.
Update Network Adapter Driver: Enhance WiFi Performance
If you're experiencing slow WiFi on your Windows PC, outdated or incompatible network adapter drivers could be the culprit. Here's how to update them:
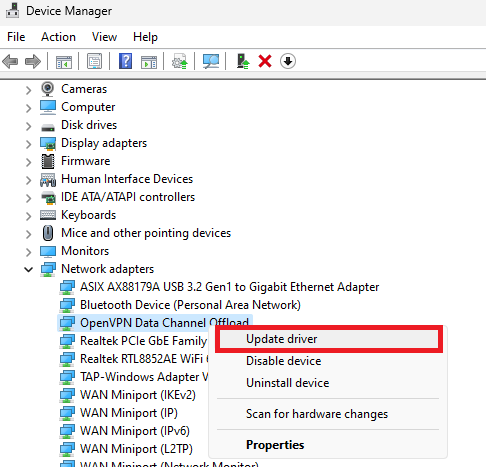
Open Device Manager: Use the start menu search to find and open 'Device Manager'.
Find Your Network Adapter: Expand the 'Network Adapters' section. Right-click the network adapter you're using, usually labeled as 'Wi-Fi' or with a specific model name.
Update Driver: Click “Update Driver,” then choose 'Search automatically for updated driver software.' Wait a moment for Device Manager to download and install the latest update. This can help your WiFi connection run smoother, particularly during bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming or online gaming.
Eliminate Dead Spots: Extend Your WiFi Signal
If there are areas in your home where the WiFi signal is weak or non-existent, WiFi extenders or repeaters can be a solution:
Consider a WiFi Extender: These devices amplify and extend your WiFi signal, covering larger areas. For example, if you have a room that struggles to maintain a stable connection, placing an extender halfway between the router and that room can create a seamless online experience.
Choose the Right Product: Different extenders have varying ranges and features. Consider your needs and the layout of your home when making a selection. Some extenders even offer advanced features like dual-band support or seamless roaming.
By ensuring your network adapter drivers are up-to-date and strategically using extenders, you can achieve a robust and reliable WiFi connection throughout your home.
Device Manager > Network Adapters > Update Driver
-
Open 'Device Manager,' expand 'Network Adapters,' right-click your network adapter, click “Update Driver,” and search automatically for updated driver software.
-
WiFi extenders or repeaters amplify and extend your WiFi signal, covering larger areas of your home. They're ideal for eliminating weak or dead spots.
-
Use the 'Task Manager' in Windows, click the 'Network' label, and identify apps consuming network resources. Right-click to end processes that won’t break your operating system.
-
Updating your router's firmware enhances its overall performance and security. Check your router's web settings by searching your router model in your browser.
-
Yes, devices like phones and microwaves can interfere with the WiFi signal. Consider switching to a 5GHz band if available or keep these devices away from the router.